Polyamide 6 for Weight Reduction and Metal Replacement
Weight reduction is a crucial factor in product design in certain markets such as aviation and automotive, with the goal of reducing fuel consumption, CO2 emissions, and improving dynamic performance.
To achieve this reduction, the PROMYDE PA6 range offers two main approaches:
- Development of lighter polymers: The aim is to develop engineering polymers with properties similar to those of currently used materials but with lower density.
- Substitution of higher density materials with technical engineering polymers: This involves replacing heavier materials, such as metals, with technical polymers that meet the required properties.
Lightweight polyamides 6 for weight reduction
PA6 Nano Clay (NC)
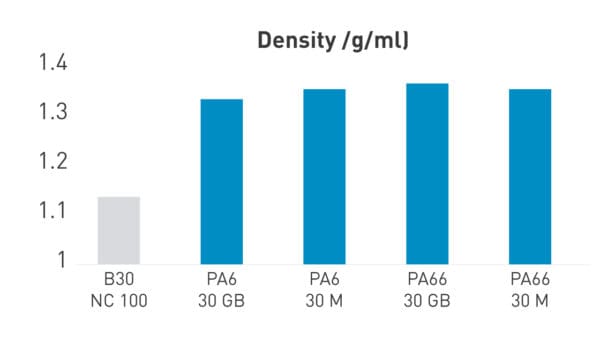
Reinforced grades with PROMYDE Nano Clay contain clay nanoparticles embedded in the polymer matrix, improving properties and reducing weight.
PA6 Weight Reduction (WR)
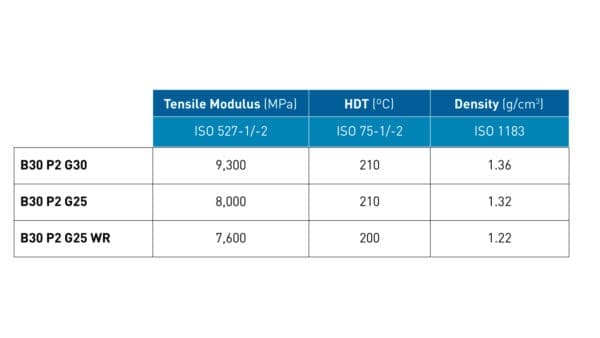
Our WR grades offer a lighter alternative for weight reduction while maintaining the same properties as conventional materials.
PA6 reinforced with Hollow Beads (HB)
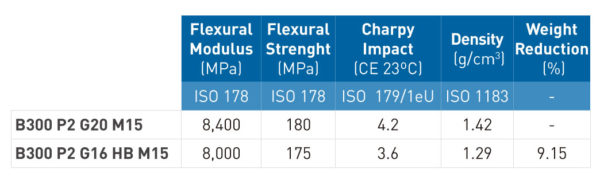
PROMYDE HB grades use hollow glass beads as reinforcement, providing an additional weight reduction of up to 20%.
PA6 for Replacing Heavy Materials in Differents Areas
- Substitution of metals with electrically, thermally and electrically & thermally conductive polymers.
- Substitution of metals with solutions with high modulus and resistance to high temperatures.
- Substitution of solid parts with hollow alternatives manufactured through water or gas-assisted injection.
In summary, PROMYDE offers a wide range of options for weight reduction in injection-molded parts, providing benefits in terms of energy efficiency and performance.
applications

Electric Vehicle
We have been working for years on the development of specific engineering polymers for electric vehicles, providing solutions to new challenges, such as improving their autonomy, safety and sustainability.

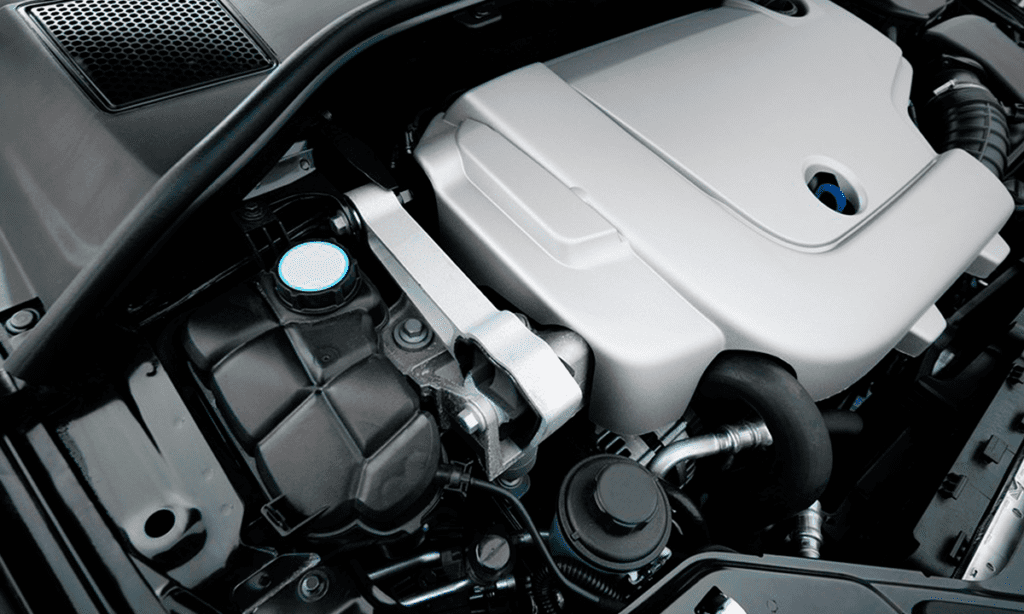
Underhood Applications
The Promyde range of materials provides solutions for all types of underhood applications requiring high temperature stability and hydrolysis resistance, while maintaining their mechanical properties.

Train interior
NUREL offers specialized PA, PBT, PET, and PBT/PET compounds for train component solutions, including connections and cables. These compounds are UL94 certified and compliant with HL3 according to the EN45545 standard.
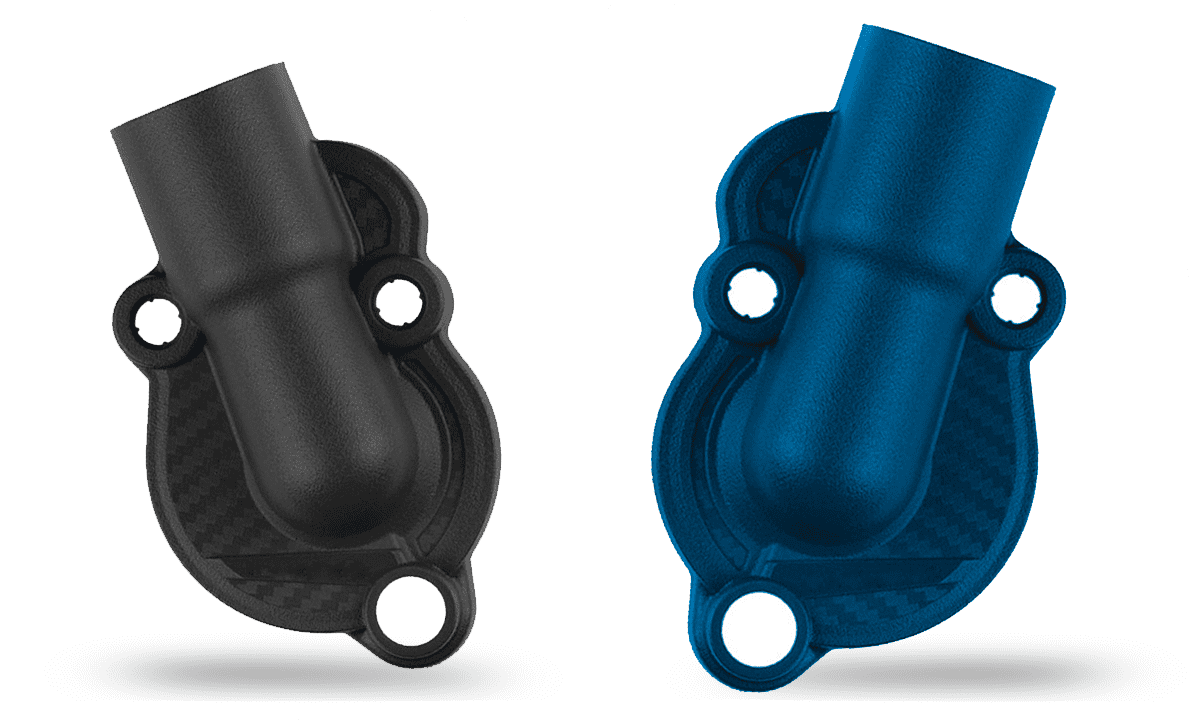
Structural reinforced parts
Vehicle structures, such as handgrips, require specific high flow and surface finish solutions that allow temperature dissipation for proper operation.
RELATED MARKETS
MOBILITY AND AUTOMOTIVE
Mobility and transportation has always been a leader in innovation for mechanical developments and process performance improvements. Thanks to our range of engineering polymers, NUREL participates in this race of continuous development with our offer in PA6, PA66, PBT and PET.

INDUSTRIAL
Industrial sector demands special performance to meet the most demanding efficiency, durability and resistance requirements. Promyde® and Recomyde® polymers and composites provide technical and value-added solutions in the manufacture of industrial machinery and components.
OTHERS SOLUTIONS
Want to stay updated on the latest on NUREL Technical Polymers?
Subscribe to the Newsletter








